
The Vision vs. Reality
The Halton Mobility Management Strategy presents a transformative vision for the region’s transportation infrastructure. However, upon closer examination, it becomes evident that this vision may be more aspirational than achievable. Halton Hills, characterized by its suburban and semi-rural nature, is not the ideal candidate for the ambitious scale of mobility transformation proposed. This article critically examines the assumptions underlying the strategy, particularly the feasibility of achieving such aggressive growth targets and the practicality of implementing urban-focused mobility solutions in a region like Halton.
Overestimating Population Growth: A Flawed Foundation
Central to Halton’s strategy is the assumption of significant population and employment growth, with projections of both doubling by 2041. These projections appear overly optimistic, especially in light of broader demographic trends. Globally, declining birth rates, particularly in developed countries like Canada, challenge the assumption that Halton will continue to experience rapid growth. While the strategy projects a booming population, it does not fully consider the implications of a potentially shrinking or aging population on transit usage and infrastructure needs.
Moreover, the strategy fails to address the reality that Halton’s suburban layout and low-density development are unlikely to support the high-frequency transit services envisioned. This disconnect between population growth projections and actual demographic trends raises serious concerns about the strategy’s viability.
Overestimating Population Growth: A Flawed Foundation
Halton’s strategy leans heavily on urban mobility solutions, such as mobility-as-a-service and high-frequency transit corridors, concepts that are primarily designed for dense urban environments. Applying these solutions to Halton, a region with a strong car culture and low-density development, is misguided. The strategy underestimates the deeply ingrained car dependency in suburban areas like Halton. Shifting commuter habits from personal vehicles to public transit has proven challenging in similar regions, and there is little evidence to suggest that Halton will be an exception.
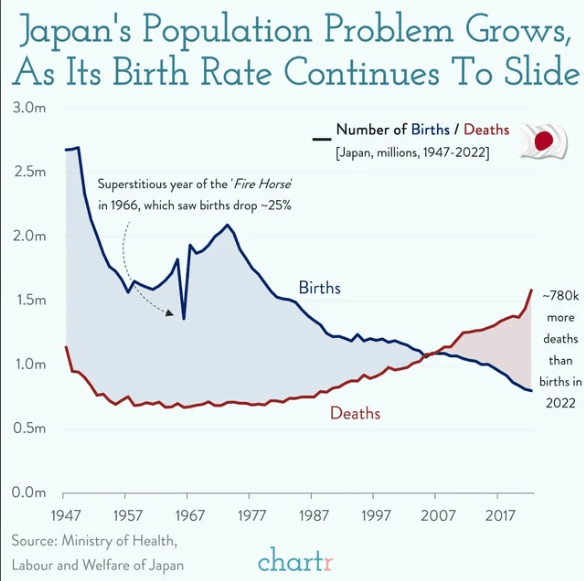
Declining Birth Rates
The following chart vividly illustrates Japan’s deepening demographic crisis, characterized by a sharp decline in birth rates and a rising death rate over the past several decades. From the late 1940s through the 1960s, Japan experienced a significant drop in the number of births, which was particularly pronounced during the superstitious “Fire Horse” year of 1966, where births plummeted by around 25%. This period marked the beginning of a long-term trend of declining births.
As the chart shows, while births briefly stabilized, they never returned to previous highs. Over time, as the population aged, the number of deaths began to rise steadily. The crossover point, where deaths began to outnumber births, occurred around 2007. This trend has only accelerated, leading to a situation where in 2022, there were approximately 780,000 more deaths than births.
This stark demographic shift is a powerful indicator of the challenges Japan faces as it contends with an aging population and a shrinking workforce. The consequences of this imbalance are far-reaching, affecting economic growth, social services, and the sustainability of the population. Japan’s experience serves as a critical case study for other nations that may face similar demographic challenges in the future. The chart underscores the urgency of addressing birth rates and developing policies that can mitigate the long-term impacts of population decline.
Additionally, the focus on technology-based solutions, while innovative, does not address the fundamental issues of infrastructure and service inadequacies. These technologies, such as autonomous vehicles and ride-sharing, are still in their infancy and may not deliver the promised benefits within the strategy’s timeframe.
The Reality We Are Not Talking About
In stark contrast to Japan’s declining population, Canada, particularly Ontario, has experienced a significant population boom in recent years. This growth has been largely driven by an aggressive immigration policy, which many have criticized as being far out of hand. The surge in population has resulted in increased demand for housing, infrastructure, and social services, putting pressure on local resources and leading to a housing market that has become increasingly unaffordable for many Canadians.
However, this trend may be poised for a dramatic shift. With the potential change in government and the Conservative Party’s rising influence, there is a strong indication that immigration policies could be tightened significantly. The Conservatives have been vocal about their intent to “lock down” what they perceive as an immigration overflow, aiming to reduce the strain on housing and other public services.
If such changes are implemented, the demand for homes is expected to diminish, easing the current housing crisis to some extent. This potential policy shift could lead to a more balanced housing market, but it also raises questions about the long-term economic and demographic impacts of restricting immigration, especially in a country that has historically relied on it to drive population growth and economic vitality. The upcoming changes could redefine the future trajectory of Canada’s population and housing needs, making it a pivotal issue in the nation’s political landscape.
Infrastructure Neglect: A Recipe for Disaster
A glaring omission in Halton’s strategy is the lack of focus on existing infrastructure. Before embarking on expansive new projects, it is crucial to address the current deficiencies in Halton’s transportation infrastructure. Many transit systems across North America are grappling with significant maintenance backlogs, and Halton is no exception. Ignoring these issues in favor of ambitious new projects is a recipe for disaster.
The consequences of infrastructure neglect are evident in recent catastrophic failures, often hastily attributed to climate change when, in reality, they result from years of underinvestment and poor maintenance. Halton would be better served by prioritizing the improvement and maintenance of its current transit services. Enhancing the reliability and frequency of existing bus routes would build ridership and trust, laying a more solid foundation for future growth.
Financial Realities: The Cost of Ambition
The strategy’s ambitious goals come with a significant price tag, yet there is little clarity on how these projects will be funded. Securing long-term, stable funding for transit initiatives has been a persistent challenge in Canada, and Halton is unlikely to be an exception. The strategy does not adequately address this challenge, relying instead on optimistic projections and the assumption that funds will materialize.
A critical review of the budget reveals alarming plans for hefty expenditures in the coming years, despite the looming economic downturn. With the economy already in decline and expected to worsen, these financial projections seem increasingly detached from reality. As mortgages locked in during the favorable interest rates of 2019 and 2020 come due, a massive economic upheaval is expected. This financial strain will likely limit the availability of funding for ambitious projects like those proposed in Halton’s strategy.
Ontario’s Track Record With Similar Projects
Ontario has a long history of ambitious infrastructure projects that have aimed to transform urban transit across the province. However, these projects have often been marred by significant cost overruns, delays, and ongoing operational challenges. As the province continues to invest in major transit expansions, it’s essential to reflect on past experiences to better understand the risks and complexities involved. The following examples highlight some of Ontario’s most notable transit projects, each of which encountered hurdles that serve as important lessons for future infrastructure planning and execution.
Toronto-York Spadina Subway Extension
This project, which extended Toronto’s Line 1 subway to Vaughan, faced significant cost overruns and delays. Originally budgeted at $2.6 billion with a completion date of 2015, it ultimately cost about $3.2 billion and opened in December 2017.
Eglinton Crosstown LRT
This light rail project in Toronto has experienced multiple delays and cost increases. Initially slated to open in 2020 at a cost of $5.3 billion, it is now expected to open in 2024 with costs potentially exceeding $12 billion.
Ottawa LRT (Phase 1)
Ottawa’s Confederation Line opened more than a year late in 2019 and has faced ongoing reliability issues. While the final cost remained close to the $2.1 billion budget, the delays and performance problems have been significant.
Montreal’s REM (Réseau express métropolitain)
This light rail project has seen its budget increase from an initial $6.3 billion to over $7.8 billion. The opening of its first segment was delayed from 2021 to 2023, with full completion now expected in 2027 instead of 2024.
Vancouver’s Broadway Subway Extension
While still under construction, this project has already seen its budget increase from $2.83 billion to $3.1 billion, partly due to pandemic-related challenges.
Winnipeg’s Southwest Transitway
The second phase of this bus rapid transit project opened in 2020, about $38 million over its original $467 million budget.
This light rail project has seen its budget increase from an initial $6.3 billion to over $7.8 billion. The opening of its first segment was delayed from 2021 to 2023, with full completion now expected in 2027 instead of 2024.
Economic Downturn: A Threat to Sustainability
If the economy continues to decline, Halton Hills could face several financial risks, including:
- Increased Debt Charges: The capital budget plans for $55.3 million in long-term external debt financing. Economic downturns typically lead to higher interest rates, which could significantly increase the cost of borrowing and burden the town’s fiscal position.
- Funding Shortfalls: Significant capital projects, like Gellert Phase 2 and the Transit Service Strategy, are contingent on alternative funding sources such as external funding or special levies. A worsening economy might limit these opportunities, delay critical projects, or force the town to seek new, potentially more costly financing options.
- Reduced Development Charges: Economic downturns can slow down development activities, leading to a reduction in development charges—a key source of funding for growth-related capital expenditures. This would impact the town’s ability to finance new infrastructure projects needed to accommodate growth.
- Escalating Project Costs: The budget has already identified rising construction costs and increased investment needs for the state-of-good-repair program. An economic downturn could further exacerbate these costs due to inflation or supply chain disruptions.
- Pressure on Reserves: The town relies heavily on its capital reserves to fund its capital program. A worsening economy could deplete these reserves faster than anticipated, especially if revenues fall short or emergency expenditures arise.
- Decreased Revenue Streams: General economic decline can lead to lower tax revenues and other local government incomes, further straining the town’s budget and its ability to maintain and upgrade existing infrastructure.
To mitigate these risks, the town must reassess its capital priorities, consider more conservative fiscal policies, and develop contingency plans for further economic contraction. Maintaining budget flexibility will be crucial to adapting to rapidly changing economic conditions.
A Call for Pragmatism and Fiscal Responsibility
The Halton Mobility Management Strategy is undeniably ambitious, but it is also deeply flawed. Its assumptions about population growth, the suitability of urban mobility solutions in a suburban context, and the neglect of existing infrastructure all point to a plan that may be more aspirational than realistic. The town would be better served by focusing on fixing and supporting current infrastructure rather than pursuing a vision that may never be realized.
With the economy poised for further decline, it is imperative that Halton Hills adopts a more conservative approach to budgeting. The town’s focus should be on maintaining existing infrastructure, ensuring financial sustainability, and prioritizing projects that deliver immediate, tangible benefits. Only by embracing a more pragmatic and fiscally responsible approach can Halton Hills hope to navigate the challenging times ahead while laying a solid foundation for future growth.

Leave a comment