
Forward:
Welcome to “Unraveling Speech Styles through Linguistic Analysis: Insights from Academic Perspectives.” This document offers valuable insights into the importance of linguistic analysis in understanding speech styles and communication approaches. By examining linguistic features such as verb frequency, noun usage, and delivery patterns of adverbs and adjectives, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of how individuals strategically employ language to communicate, persuade, and engage audiences.
This paper emphasizes the significance of an interdisciplinary approach that integrates linguistic analysis with sentiment analysis. The integrated approach enhances our ability to interpret and appreciate the richness and complexity of speech styles, paving the way for further research and deeper insights into the fascinating world of language and communication.
The theories presented in this paper have the potential to contribute to various fields such as linguistics, rhetoric, psychology, marketing, and communication studies. We hope that this document will inspire researchers to explore new avenues in analyzing language and communication styles. We invite you to delve into this informative document and discover the intricacies of speech styles through linguistic analysis.
Framing Things Up
Linguistic analysis is an invaluable tool that enables us to delve into the patterns and intricacies of speech styles. While sentiment analysis has traditionally been a prevalent approach in analyzing language, this article expands the analytical scope by focusing on linguistic features such as verb frequency, noun usage, and the delivery patterns of adverbs and adjectives. By examining these features, researchers can gain profound insights into the speaking patterns and speech styles employed by individuals, offering a comprehensive understanding of their communication approach.
Typically, sentiment analysis involves assessing the emotional tone of a text or speech, categorizing it as positive, negative, or neutral. While sentiment analysis provides valuable information about the emotional impact of a message, the inclusion of linguistic analysis broadens the analytical perspective. By scrutinizing verb frequency, researchers can discern whether a speaker employs a high volume of action-oriented language or adopts a more measured approach, indicating their propensity for emphasizing key actions or impactful moments.
Noun usage is another essential aspect of linguistic analysis, shedding light on how speakers convey their ideas and concepts. Researchers examine whether speakers employ concrete nouns, providing specific details and vivid imagery, or abstract nouns, indicating a preference for broader themes and generalizations. This analysis allows for a deeper understanding of the speaker’s inclination towards tangible examples versus more conceptual language.
The analysis of adverbs and adjectives further enriches linguistic analysis, as it elucidates the delivery patterns employed by speakers. By scrutinizing the cadence and distribution of these elements, researchers can uncover the strategies employed by speakers to create impact and evoke emotions. A nonlinear delivery, with intensifying or stair-stepping patterns of adverbs and adjectives, adds depth and engages the audience, while a more linear delivery may provide a more straightforward and direct conveyance of information.
This article approaches linguistic analysis from an academic perspective, emphasizing the significance of this approach in shedding light on distinct speech patterns and styles. By exploring the relationship between verb frequency, noun usage, and the delivery patterns of adverbs and adjectives, researchers can develop a comprehensive understanding of how individuals employ language to communicate their ideas, capture audience attention, and evoke emotional responses.
By expanding the analytical repertoire to include linguistic features, this article contributes to the academic discourse surrounding speech analysis. It highlights the multifaceted nature of communication and emphasizes the importance of considering linguistic patterns alongside sentiment analysis. Ultimately, this integrated approach enhances our ability to interpret and appreciate the richness and complexity of speech styles, paving the way for further research and deeper insights into the fascinating world of language and communication.
SPEECH#1
The characteristics of speech #1, with a lower number of adverbs overall but a concentration of them towards the end, might indicate that the speaker deliberately saves the use of adverbs for emphasizing key points or delivering a strong closing statement. By strategically placing adverbs towards the conclusion, the speaker aims to leave a lasting impression on the audience, emphasizing the importance of their message and potentially increasing its memorability.
Additionally, there are more nouns in this speech that could indicate that the speaker aims to provide a substantial and substantive argument or to present concrete evidence to support their points. By utilizing more nouns, the speaker may seek to enhance the credibility of their speech and create a sense of specificity and clarity in their message.
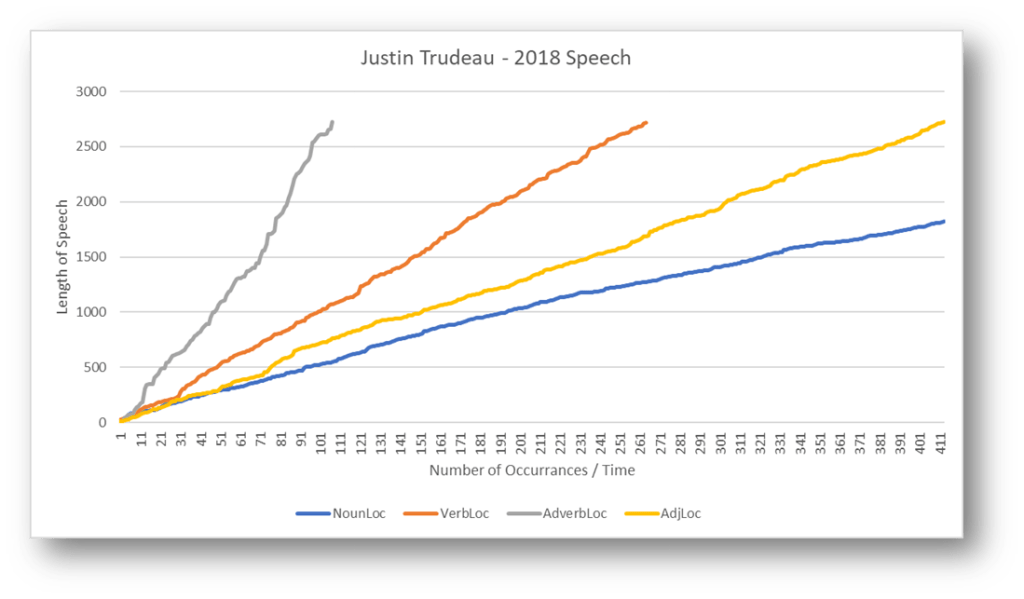
SPEECH#2
With speech #2 adverbs are almost equal in frequency or cadence to verbs, suggests a different approach. This pattern could indicate a speaker who values balance and precision in their language. The use of adverbs alongside verbs throughout the speech may serve to provide a nuanced description of actions, events, or ideas. The consistent inclusion of adverbs alongside verbs can contribute to a more detailed and expressive portrayal of the speaker’s thoughts and intentions.
The observed differences in adverb usage could reflect changes in the speaker’s rhetorical style over time. It is possible that the speaker has refined their delivery techniques or adjusted their approach to better suit evolving circumstances or audience expectations.
Conversely to speech number 1, there are less nouns used in this speech that could suggest a more abstract or conceptual approach, focusing on broader themes, ideas, or principles rather than specific instances or examples. The decreased emphasis on nouns may allow the speaker to explore more theoretical or philosophical aspects of the topic at hand.
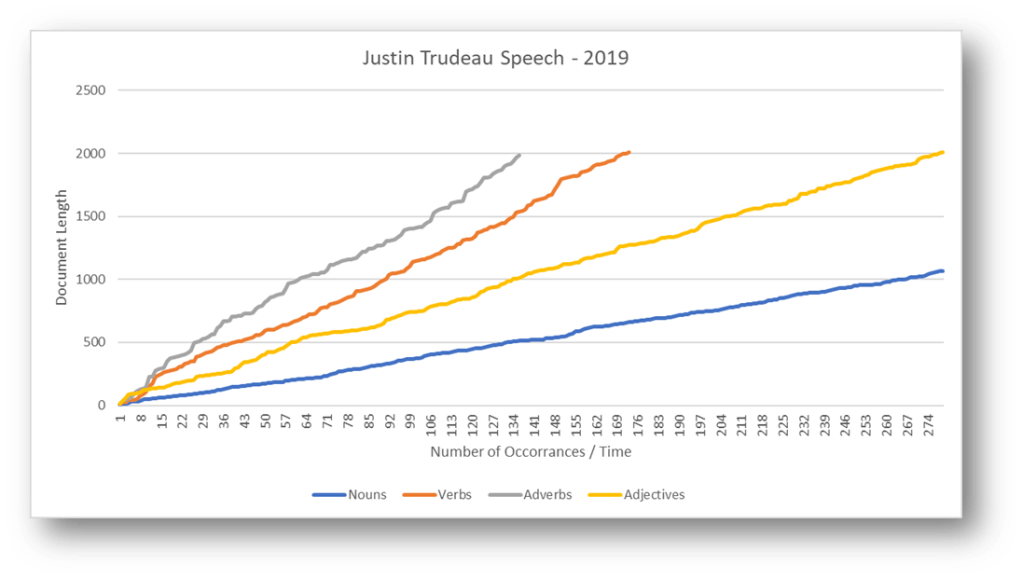
SPEECH #3 – Analysis
In this speech, a balance is struck between action-oriented language and a measured approach. Its nonlinear delivery of verbs and adverbs creates suspense and engages the audience emotionally. In terms of nouns, speech #3 presents a logical progression, providing clear explanations.
The strategic variation in pacing and emphasis during the nonlinear delivery of verbs and adverbs adds depth and intensity to the speech, allowing for moments of suspense, anticipation, and impactful highlights.
In terms of nouns, speech #3 strikes a balance between the direct and straightforward conveyance of information or ideas. The logical progression of thoughts, facts, and examples presented through nouns ensures clarity and coherence in the speech’s content.
Overall, speech #3 combines elements from both speech #1 and speech #2 while showcasing its own distinct characteristics. The careful balance between verbs, the dynamic delivery pattern, and the linear presentation of nouns demonstrate a nuanced and skillful approach to communication. This suggests that the speaker in speech #3 aims to capture the audience’s attention, deliver impactful moments, and maintain a logical and coherent structure, all while leaving a lasting impression on the listeners.

SPEECH #4 – Analysis
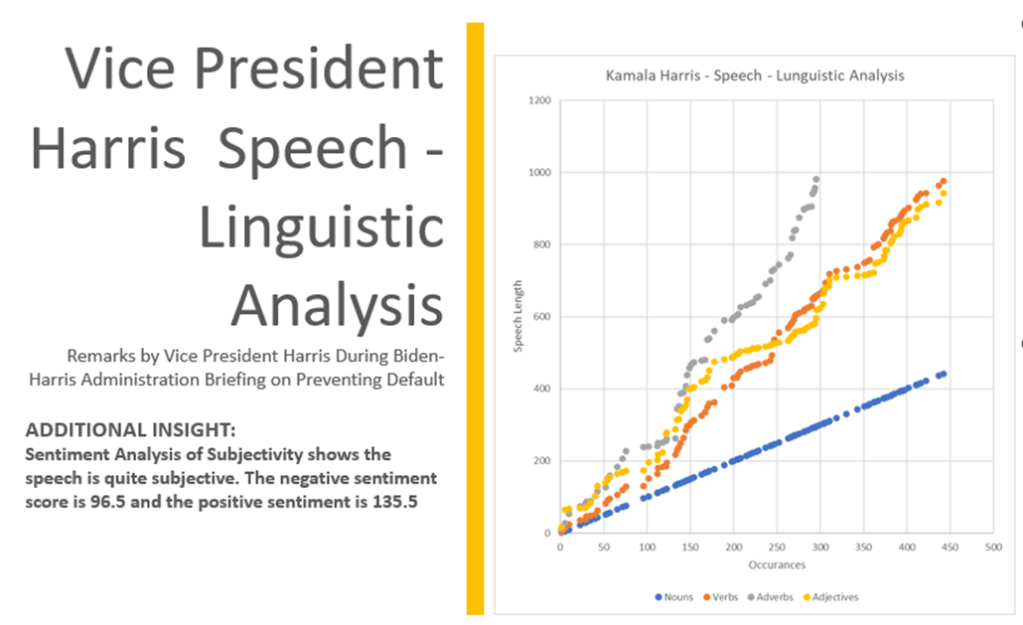
The frequency of nouns is the lowest compared to the previous speeches. This suggests a potential shift in the speaker’s communication style, where there may be less emphasis on specific objects, ideas, or entities. The reduced use of nouns could indicate a preference for more abstract or conceptual language, focusing on broader themes or principles rather than concrete examples.
Regarding verbs and adjectives, their volumes are closely aligned and follow a similar pattern of usage. The pattern is characterized by non-linearity, featuring frequent fluctuations between low and high usage. These sharp rises in verb and adjective usage could indicate moments of heightened intensity, emphasizing impactful actions or vivid descriptions. The speaker may strategically deploy these linguistic elements to create a dynamic and engaging delivery that captures the audience’s attention and evokes strong emotional responses.
Likewise, the use of adverbs is significant and follows a stair-stepping pattern throughout the speech. This pattern suggests a deliberate strategy of increasing the presence of adverbs in four distinct steps. Each step likely corresponds to specific sections or moments in the speech where the speaker intends to enhance emphasis, clarity, or persuasion. By strategically introducing adverbs in these increments, the speaker aims to maintain the audience’s engagement and reinforce key points at strategic intervals.
Overall, this speech exhibits a linguistic style that deviates from linearity and incorporates patterns of increased verb, adjective, and adverb usage. This suggests a dynamic and intentional approach to communication, with a focus on impactful moments, vivid descriptions, and strategic emphasis. The lower frequency of nouns indicates a potential shift towards more abstract language. The combination of these elements reflects the speaker’s unique rhetorical strategy in this particular speech. The lower frequency of nouns might suggest a reduced emphasis on concrete details, which is an observation her critiques can pointed out on numerous occasions. The fluctuating pattern of verb and adjective usage, along with the stair-stepping pattern of adverbs, indicates a deliberate variation in the delivery style and intensity of the speech. This approach aims to captivate the audience’s attention, trigger emotional responses, and potentially drive them towards a desired action or decision.
By relying more on emotional appeal and theatrical delivery rather than presenting straightforward facts and clear concepts, this type of speech is often associated with persuasive or sales-oriented contexts. It aims to create an emotional connection with the audience, establish a sense of urgency or importance, and ultimately influence their decision-making.
The Syntax of the Analysis
Unveiling Patterns:
Linguistic analysis allows researchers to identify patterns that may reveal certain speaking patterns or speech styles. For instance, a lower frequency of verbs compared to other speeches might suggest a more measured approach, with emphasis placed on key actions or impactful moments. Conversely, a higher usage of verbs and adjectives, accompanied by fluctuating delivery patterns, may indicate a more emotional and theatrical speaking style that aims to engage the audience’s emotions and drive persuasive effects.
Noun Usage:
An examination of noun usage within speeches can offer significant insights into communication styles. A lower frequency of nouns might indicate a preference for abstract or conceptual language, emphasizing broader themes and principles rather than concrete examples. This usage could reflect a more theoretical or philosophical approach to speech delivery, focusing on overarching ideas rather than specific details.
Delivery Patterns:
Linguistic analysis also considers the delivery patterns of adverbs and adjectives, which can unveil unique speaking styles. Nonlinear or stair-stepping patterns, where these linguistic elements intensify in a non-linear fashion, often evoke dramatic effects and captivate audience attention. This approach, commonly observed in sales-oriented or persuasive speeches, aims to create emotional connections and influence decision-making through heightened intensity and theatricality.
Academic Perspectives:
From an academic perspective, linguistic analysis provides researchers with an avenue to study and understand the nuances of speech styles. By examining patterns, linguistic features, and delivery techniques, researchers can develop theories and insights into how individuals strategically employ language to communicate, persuade, and engage audiences. Such analyses contribute to academic disciplines such as linguistics, rhetoric, and communication studies, expanding our understanding of the complex interplay between language, persuasion, and audience response.
Implications and Future Research:
The application of linguistic analysis in studying speech styles holds immense potential for various domains. Understanding the linguistic choices, delivery patterns, and strategic emphasis within speeches can have implications for public speaking, political communication, marketing, and even interpersonal communication. Future research can explore the influence of linguistic styles on audience perception, the role of cultural factors in speech patterns, and the impact of linguistic strategies on persuasion and message effectiveness.
Methodology of Linguistic Analysis: Proximity, Volume, and Cadence of Linguistic Elements in Speech Patterns
In the realm of linguistic analysis, examining the proximity, volume, and cadence of various linguistic elements within a speech provides valuable insights into speech patterns and styles. This method involves the systematic counting and analysis of nouns, verbs, adverbs, and adjectives, along with their syntactic arrangements, to uncover meaningful patterns and shed light on speech characteristics such as subjectivity or verbosity.
Proximity of Nouns and Supporting Elements:
One aspect of linguistic analysis involves investigating the proximity of nouns to supporting linguistic elements within a speech. By examining the arrangement of nouns in relation to verbs, adverbs, and adjectives, researchers can discern patterns and determine the extent to which nouns interact with other components of speech. Are nouns often accompanied by descriptive adjectives or adverbs? Do they frequently appear in close proximity to verbs, indicating a strong connection between actions and objects? The proximity of nouns to supporting elements can reveal how vividly and concretely ideas are expressed, or whether a speaker relies more on abstract concepts and generalizations.
Volume of Linguistic Elements:
The volume of linguistic elements, including nouns, verbs, adverbs, and adjectives, also plays a crucial role in understanding speech patterns. By quantitatively analyzing the frequency of these elements throughout a speech, researchers can identify patterns of emphasis and determine the focal points of the speaker’s message. For example, a high volume of adjectives and adverbs may suggest an intention to evoke specific emotions or create vivid imagery. Conversely, a low volume of nouns accompanied by a higher frequency of verbs might indicate a more action-oriented and dynamic speaking style.
Cadence and Syntax:
The cadence and syntax of a speech, which refer to the rhythm, flow, and arrangement of linguistic elements, provide additional insights into speech patterns. By examining the pacing and arrangement of nouns, verbs, adverbs, and adjectives, researchers can discern whether the speech is characterized by a linear or nonlinear delivery. Does the speaker follow a consistent and smooth syntactic structure, or do they utilize a more varied and unpredictable pattern? The cadence of the speech can reveal the speaker’s intentional use of pauses, emphasis, or changes in delivery speed to engage the audience, create suspense, or highlight key points.
Supporting Findings:
The method of counting and analyzing linguistic elements, their proximity, volume, and cadence, serves as a valuable complement to other data and observations. When used in conjunction with other findings, such as subjectivity or verbosity, this method strengthens the overall analysis by providing specific linguistic evidence to support or validate those observations. It helps researchers draw more robust conclusions about speech patterns and styles, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of a speaker’s communication approach.
By employing this methodology, researchers gain a deeper understanding of how speakers utilize language to convey their messages, evoke emotions, and engage their audiences. The systematic analysis of proximity, volume, and cadence enhances our ability to interpret speech patterns and provides valuable insights into the stylistic choices speakers make, supporting broader observations and contributing to a more nuanced understanding of speech characteristics.
Sentiment Analysis:
Sentiment analysis involves the identification and classification of the emotional tone conveyed in a text or speech. By combining sentiment analysis with linguistic analysis, researchers can assess how linguistic elements, such as nouns, verbs, adverbs, and adjectives, contribute to the overall sentiment of the speech. This analysis can reveal whether the speech exhibits predominantly positive, negative, or neutral sentiments, shedding light on the emotional tone and persuasive strategies employed by the speaker.
For instance, a higher frequency of positive adjectives and adverbs in proximity to specific nouns may indicate an attempt to evoke positive emotions and create an optimistic sentiment among the audience. Conversely, a prevalence of negative adjectives and adverbs may signal an intentional use of rhetoric to evoke a sense of urgency or concern. By combining linguistic analysis with sentiment analysis, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the emotional impact of the speaker’s message.
Honesty in Speech:
Assessing honesty in speech involves understanding the truthfulness, transparency, and credibility of the speaker’s statements. While linguistic analysis alone cannot definitively determine honesty, it can provide valuable insights that complement other indicators.
Summary
Analyzing the proximity and volume of nouns, verbs, adverbs, and adjectives can uncover patterns that suggest the level of detail and specificity in the speaker’s statements. A higher frequency of concrete nouns accompanied by supporting verbs and precise adverbs may indicate a commitment to factual accuracy and a greater likelihood of conveying honest information. Conversely, excessive verbosity or the use of vague language might raise questions about the speaker’s intentions or their commitment to providing transparent and truthful communication.
When used in conjunction with other indicators, such as nonverbal cues or external evidence, linguistic analysis can help researchers assess the sincerity and honesty of a speaker’s message. However, it is essential to consider that linguistic analysis alone cannot provide conclusive evidence of honesty and should be used as part of a comprehensive approach to evaluating the credibility of a speaker’s statements.
By incorporating sentiment analysis and considerations of honesty, linguistic analysis becomes a more robust tool for understanding the emotional impact and truthfulness of a speaker’s message. This integrated approach contributes to a deeper comprehension of the multifaceted aspects of communication and facilitates a more nuanced assessment of the speaker’s style, emotional appeal, and credibility.
Linguistic analysis provides a valuable academic lens to investigate speech styles, offering insights into the patterns and techniques utilized by speakers. By examining linguistic features and delivery patterns, researchers gain a deeper understanding of how language is strategically employed to communicate, engage, and persuade. Such analyses enhance our comprehension of speech styles and contribute to various academic disciplines. With ongoing research, linguistic analysis will continue to unravel the complexities of human communication and shed light on the fascinating world of speech styles.
The integration of linguistic analysis, sentiment analysis, and considerations of honesty within speech analysis can provide a comprehensive understanding of the speaker’s communication style and the underlying emotional and truthful aspects of their message.
The integration of linguistic analysis, sentiment analysis, and considerations of honesty within the analysis of spoken language offers a valuable toolkit for understanding communication patterns and assessing the emotional impact and truthfulness of a speaker’s message. By systematically examining the proximity, volume, and cadence of linguistic elements, researchers gain insights into speech styles, emotional appeals, and potential indicators of credibility.
This comprehensive approach warrants further study and exploration. The complex interplay between linguistic features, sentiment, and honesty in spoken language requires in-depth investigation to refine methodologies, establish robust frameworks, and uncover new insights. Further research can delve into specific domains, such as political speeches, courtroom testimonies, or persuasive marketing, to explore how linguistic analysis enhances our understanding of communication dynamics and its influence on audience perceptions.
By expanding our understanding of linguistic patterns, sentiment, and honesty within spoken language, we can improve our ability to interpret, evaluate, and respond to various forms of communication. This research can have practical applications in fields such as public speaking, political discourse analysis, deception detection, and human-computer interaction.
In light of the significance and potential impact of this interdisciplinary approach, further study is essential to refine existing methodologies, explore new avenues of analysis, and validate findings across different contexts and languages. Advancing our understanding of spoken language through linguistic analysis and its integration with sentiment analysis and considerations of honesty can equip us with valuable tools to comprehend the intricacies of human communication more deeply.
In summary, the integration of linguistic analysis, sentiment analysis, and considerations of honesty provides a comprehensive toolkit for understanding speech patterns, emotional impact, and truthfulness. By analyzing the proximity, volume, and cadence of linguistic elements, researchers gain valuable insights into communication styles, sentiment, and credibility. Linguistic analysis complements other data and observations, strengthening the overall analysis and supporting robust conclusions about speech patterns and styles. Incorporating sentiment analysis helps assess the emotional impact of linguistic elements, while considerations of honesty contribute to evaluating the truthfulness and transparency of a speaker’s statements. This integrated approach warrants further study to refine methodologies, explore new applications, and deepen our understanding of human communication. It holds practical implications in various fields, from public speaking to deception detection, and encourages ongoing research to advance our knowledge of linguistic patterns, sentiment, and honesty within spoken language.

Leave a comment